Load Testing Using Jmeter

In this blog post, we'll compare commonly used testing tools and delve into the basics of JMeter, a popular choice in backend development for performance testing. We'll cover its installation, basic components, and how to interpret aggregate reports from tests.
The Importance of Load Testing in Backend Development
In the world of backend development, load testing is not just a best practice—it's a necessity. But why is it so important? At its core, load testing is all about ensuring that your applications can not only survive but thrive under the heavy demands of real-world use. It's a process that rigorously tests the application's performance, particularly under high traffic or data processing conditions. This is vital because it helps identify how the application behaves when pushed to its limits, revealing key areas like response times and overall throughput.
One of the most significant benefits of load testing is its ability to pinpoint bottlenecks—those frustrating choke points that can slow down or even halt operations. These might lurk in your database, within your application code, or in the server configuration, and uncovering them is essential for smooth performance. Furthermore, it's not just about finding problems but also about verifying stability. Load testing ensures that your application won't crumble under pressure, offering a stable and reliable experience for your users, which is paramount for maintaining their trust and satisfaction.
But there's more to it than just keeping things running smoothly. Load testing also plays a crucial role in infrastructure planning and cost management. By understanding how your application fares under different loads, you can make informed decisions about the infrastructure needed to support your user base effectively. This foresight helps in optimizing resource utilization, preventing unnecessary expenditure on over-provisioning.
Moreover, in industries where performance is tied to regulatory compliance or service level agreements (SLAs), load testing is indispensable. It's a tool that ensures you're not just meeting but exceeding the benchmarks set for performance, keeping you in line with industry standards and customer expectations.
In a distributed system, load testing the program is also crucial to give feed back on flawed code logic to prevent critical business losses. For example, if a discount code is supposed to be only issued 100 times, but in a distributed system, race conditions may occur without proper resource management and may cause an over issue of the discount code. This kind of logical flaws are not discoverable in normal testing environments. To prevent this kind of scenario from happening, we will use a Distributed Mutual Exclusion solution like zookeeper, redis
Finally, in our competitive digital landscape, the performance of your application can set you apart. Load testing prepares your application to handle peak demands, ensuring it remains competitive, robust, and ready for whatever challenges the market throws its way. In essence, load testing is about being proactive, not reactive—it's about preparing for success in a digital world that never slows down.
Common Testing Tools Compared
-
LoadRunner
- Known for stable performance and detailed test results.
- Customizable scripts for load testing.
- Complex with many features, which can be overwhelming.
-
Apache AB (Ideal for Single Interface Load Testing)
- Simulates multi-threaded concurrent requests.
- Low resource requirements on the testing machine.
- Can significantly load the target server, sometimes used for simple DDOS attacks.
-
Webbench
- Forks multiple child processes for web access testing.
- Each child process reports back to a parent process for final results compilation.
-
Jmeter
- Open-source and free, widely used in internet companies.
- Supports testing various protocols and applications like HTTP(S), SOAP/REST Web services, FTP, JDBC, LDAP, JMS, SMTP(S), POP3(S), IMAP(S), and TCP.
- User-friendly for beginners, yet offers high performance.
- Java-based with capabilities for functional testing, stress testing, distributed testing, and more.
- Provides data analysis and various reporting formats.
Quick Installation of JMeter 5.x
- Requires JDK 8 or above.
- JDK is recommended over JRE for HTTPS testing, as JDK includes the keytool utility.
- Download from JMeter official site.
- Installation guide available at JMeter User Manual.
There seems to be a issue when running Jmeter that is install with Homebrew on macOS sonoma
The solution that worked for me is discussed in this thread
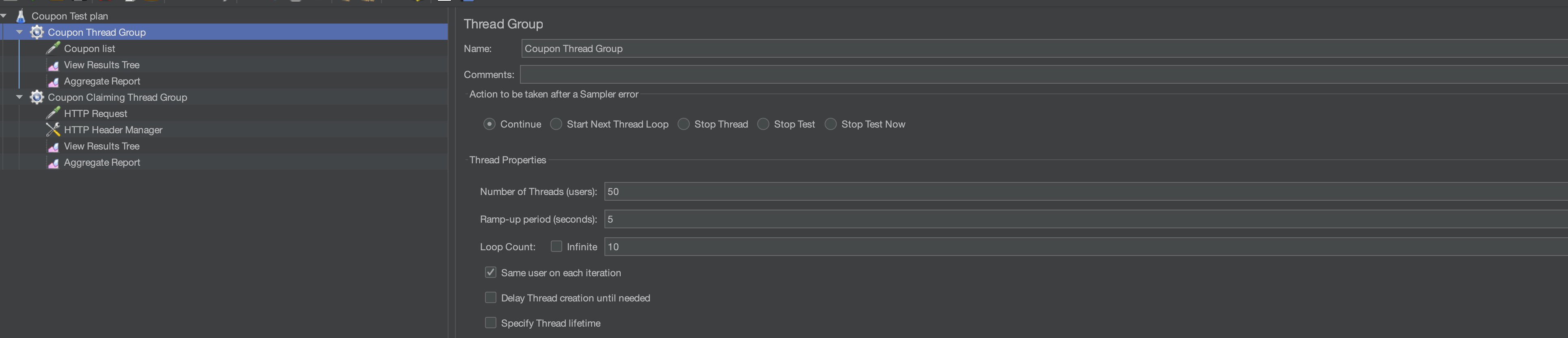
JMeter 5.x Basics: Thread Groups and Samplers
Thread Groups (Controls Overall Concurrency)
- Number of Threads: Represents the number of virtual users.
- Ramp-Up Period: Time taken for all threads to start (e.g., 100 threads in 20 seconds means 5 threads start every second).
- Loop Count: Number of requests each thread will send.
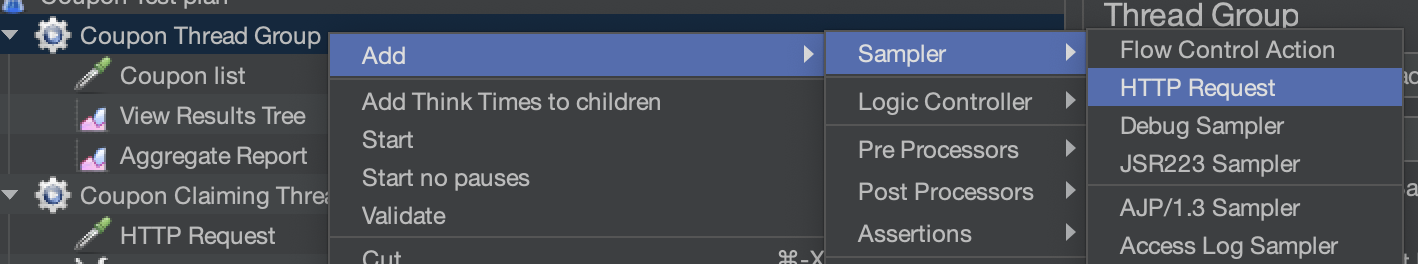
Samplers (HTTP Sample Under a Thread Group)
How to create a HTTP sampler
How to use it
- Name: Identifier for the sampler.
- Comments: Description of the sampler.
- Web Server Settings:
- Protocol (usually HTTP).
- Server name or IP.
- URL path.
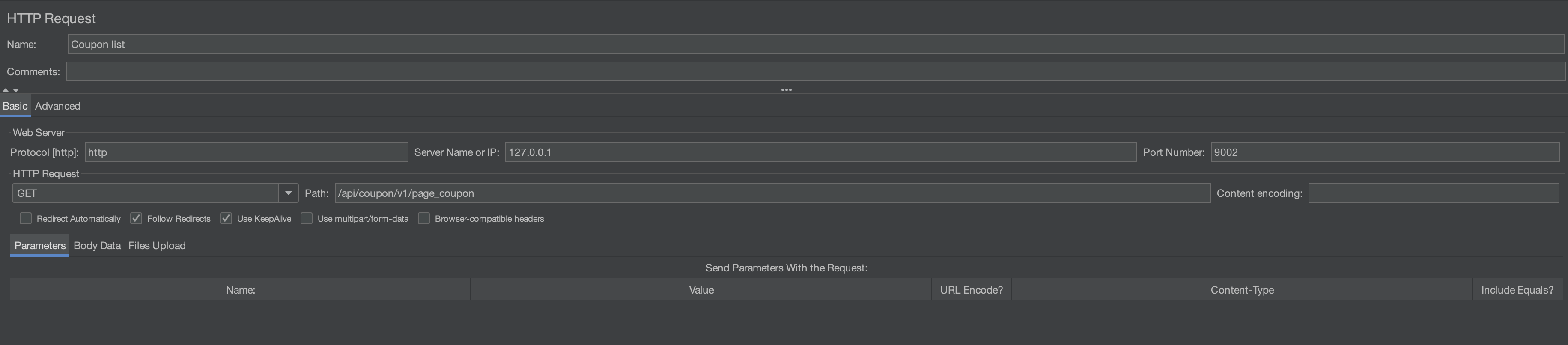
This part you can just fill in like a postman request, they have the relevant fields for a http request
Test Results
- Add listeners like 'View Results Tree' and 'Aggregate Report' under the thread group for results analysis.
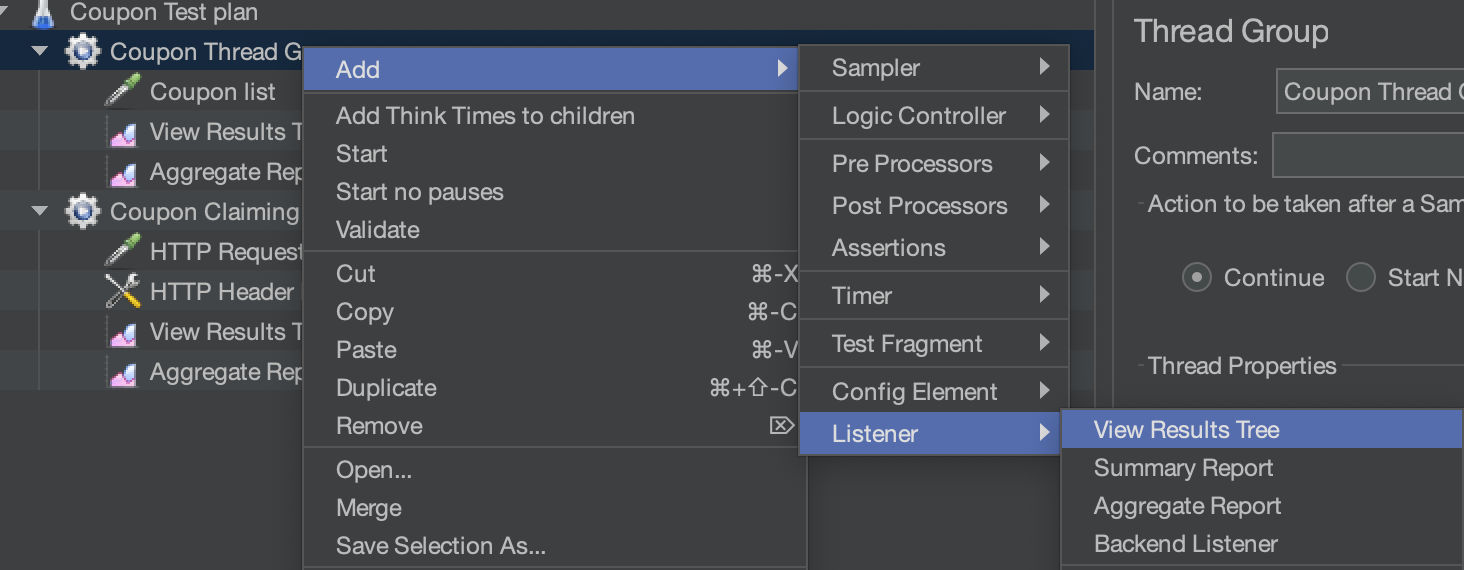
Execute the test plan
In the menu bar, click on the start button and jmeter will start the testing plan.
As the program executes, you can see the relevant outputs in the View Result Tree and Aggregate Report
Interface Load Testing and Aggregate Report Analysis
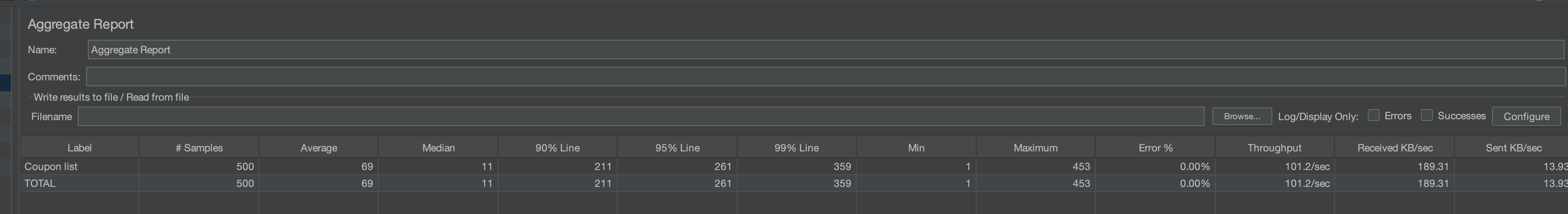
Aggregate Report Components
- Label: Name of the sampler.
- Samples: Total number of requests sent.
- Average, Median: Average and median response times.
- 90%, 95%, 99% Line: Response times for 90%, 95%, and 99% of users.
- Min, Max: Minimum and maximum response times.
- Error%: Percentage of error requests.
- Throughput: Requests per second.
- KB/Sec: Data received per second.
Things to take note
- Adding extra listeners will take up system resources and hence affecting the test effeciency
- The GUI is just a simple way to construct the test plan, for the actual testing, you should not use the test plan
Conclusion
Understanding these tools and how to use them effectively is crucial for backend developers. JMeter, with its versatility and user-friendliness, stands out as a powerful tool for various testing scenarios. By mastering these tools, developers can ensure the performance and reliability of their backend systems.