Introduction to seata

Introduction to Seata
Seata is an open-source distributed transaction framework initially started by Alibaba's middleware team under the name Fescar, which was later renamed to Seata. It aims to provide high-performance and easy-to-use distributed transaction services in a microservices architecture.
Reasons for Choosing Seata
- Backed by Alibaba: With the support of Alibaba's dedicated team for promotion and technical development, Seata ensures robust and reliable solutions.
- Proven Track Record: It has been widely used in production environments without significant issues, notably supporting Alibaba's ecosystems during high-traffic events
- Integration with Mainstream Microservices Frameworks: Seata seamlessly integrates with popular microservices frameworks, making it a versatile choice for various architectures.
- Active Community and Comprehensive Documentation: The high activity in its community and the availability of detailed documentation make it a user-friendly option.
- Commercial Product Support with GTS: Alibaba Cloud's commercial product, GTS, offers seamless migration and support for Seata, enhancing its usability in enterprise environments.
- Support different mode like AT,TCC and sage
Seata's Core Components
-
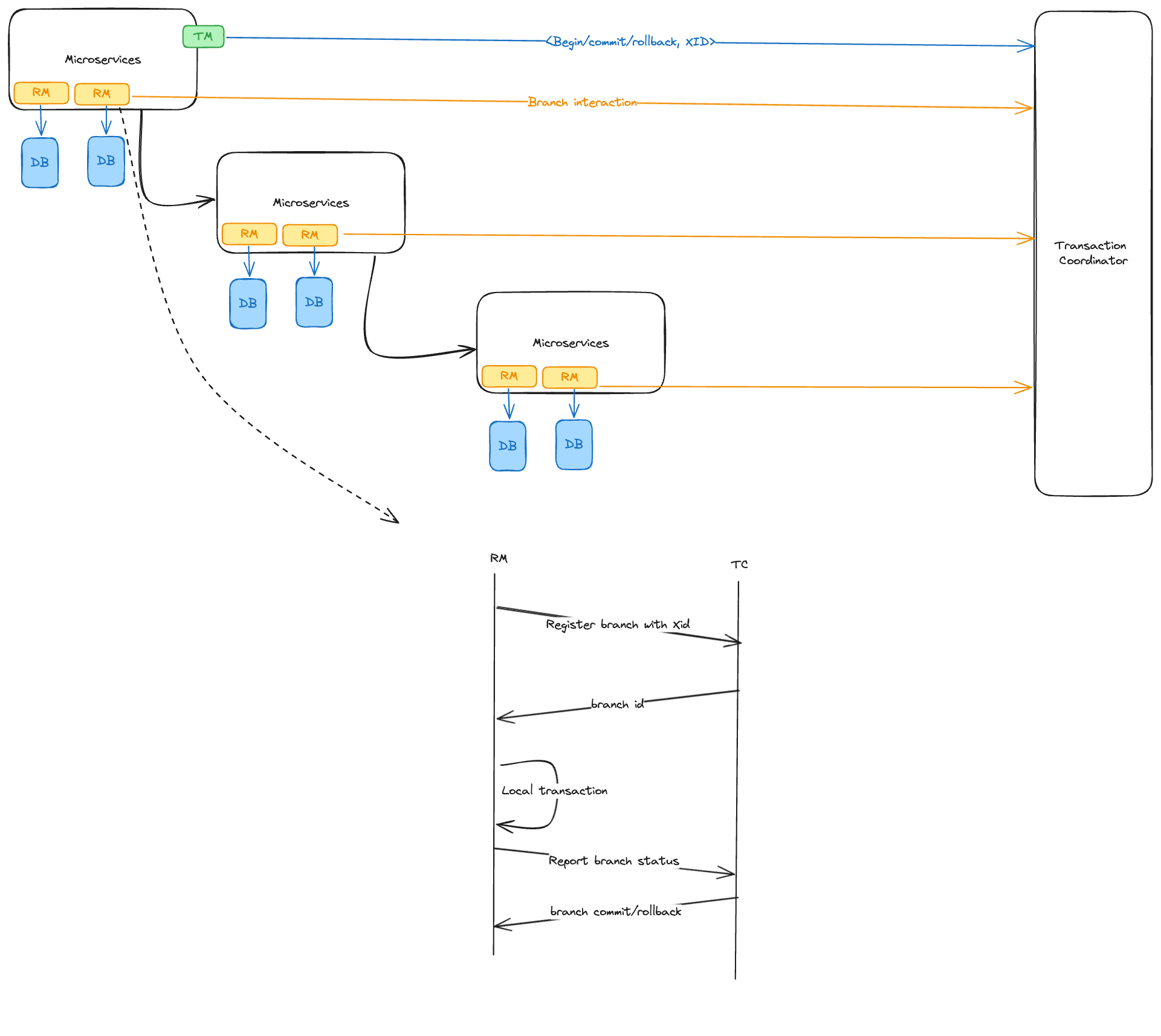
TC (Transaction Coordinator): Manages the state of global branch transactions and is responsible for the global transactions' commit or rollback.
-
TM (Transaction Manager): Handles the initiation, committing, or rolling back of global transactions.
-
RM (Resource Manager): Manages resources on the branch transaction level, registering branch transactions with the TC, reporting their status, and carrying out commit or rollback commands from the TC.
Unique Feature: XID
Seata introduces the concept of an XID (Global Transaction ID), generated by the TC when a global transaction is initiated by the TM. This XID is propagated across microservices in the call chain, linking multiple sub-transactions together.
Transaction Process in Seata
- Transaction Initiation: A TM in Service A requests the TC to begin a global transaction, which generates a unique XID.
- Branch Registration: Service A's RM registers a branch transaction with the TC.
- Database Operations: Service A performs database operations as part of its branch transaction.
- Service Invocation: Service A invokes Service B, propagating the XID in the microservice call chain context.
- Branch Inclusion: Service B's RM registers a branch transaction with the TC, incorporating it into the global transaction associated with the XID.
- Completion and Resolution: After the transaction chain completes, the TM decides to commit or rollback the global transaction based on the outcome, instructing the TC accordingly.
- TC Coordination: The TC then orchestrates all the branch transactions under the XID to commit or rollback.
Key Role of UNDO_LOG
Seata utilizes the UNDO_LOG table, a rollback log record table, as a critical component for implementing distributed transactions. This table, created in each application's database requiring distributed transactions, stores before-and-after data images as rollback logs, enabling transactions to be rolled back in case of anomalies.
CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'increment id',
`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT 'branch transaction id',
`xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT 'global transaction id',
`context` varchar(128) NOT NULL COMMENT 'undo_log context,such as serialization',
`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL COMMENT 'rollback info',
`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '0:normal status,1:defense status',
`log_created` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT 'create datetime',
`log_modified` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT 'modify datetime',
`ext` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'reserved field',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='AT transaction mode undo table';
Conclusion
Seata stands out as a robust, reliable, and versatile solution for managing distributed transactions in microservices architectures. Its design, backed by Alibaba's expertise, provides a comprehensive solution for developers facing the challenges of maintaining data consistency across distributed services. With its active community, comprehensive documentation, and compatibility with various transaction modes, Seata is well-positioned to be a go-to framework for organizations aiming to implement efficient and reliable distributed transaction systems.